Our Services

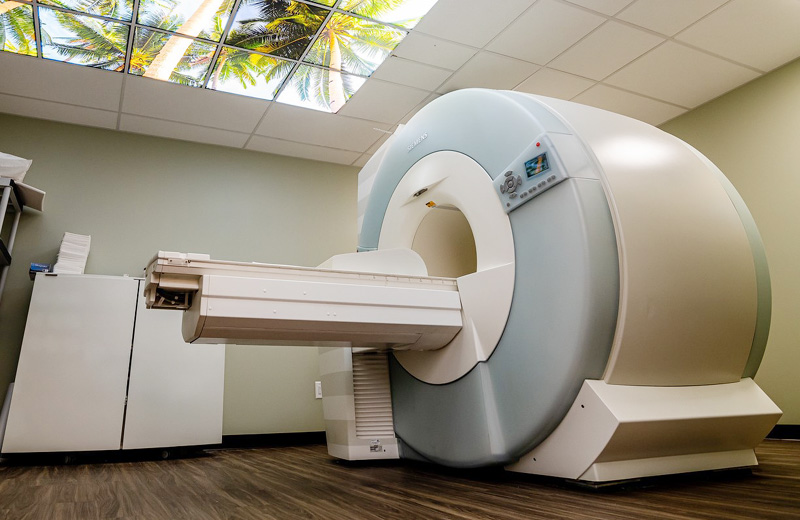
What is MRI?
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a special diagnostic test that produces very clear, detailed pictures of internal organs and structures in your body. The test uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves, and a computer to create images in cross-sections. While an X-ray is very good at showing bones, an MRI lets your health care provider see structures made of soft tissue, such as tendons, bone marrow, ligaments and cartilage, and organs in your chest, abdomen, and pelvis.
When is it used?
Health care providers use MRI to diagnose problems in the brain and spinal cord, to see the size and location of tumors. It is often used to fully visualize and diagnose problems within your joints and other soft tissues. MRI is also helpful in diagnosing diseases and disorders of the eyes and ears. For example, an MRI may show whether you have torn ligaments or torn cartilage in your knee and help your health care provider decide whether you need surgery. It is also useful for injuries involving the shoulder, back, or neck.
What happens during an MRI procedure?
You will lie down on a cushioned bed that moves into a donut-shaped apparatus that is open on both ends. If you get nervous when you are in small closed spaces, you can opt to have your MRI performed in a Wide-Open MRI which gives extra space around your body, or an Open MRI that is a less enclosed space. Talk to your health care provider about this before you have your MRI.
For some MRI scans, a contrast medium (gadolinium) is injected to highlight certain tissues for closer examination. This type of scan helps differentiate between healthy and diseased tissue, making it possible to accurately diagnose many diseases in their early stages.
Most MRI studies take between 30 and 60 minutes and you will be able to communicate with the technician during the procedure. You may hear loud sounds while the pictures are taken. However, for patient comfort, we provide all patients with earplugs so that the noise is
dampened. When the test is over you may go home. Your referring doctor will schedule a visit with you to discuss the results of your test.
What are the benefits and risks of an MRI procedure?
An MRI is able to visualize internal organs that are difficult or impossible to see with other diagnostic exams. There is no radiation, the exam is painless, and there are no harmful side effects.
What are my options?
MRI scanners come in different magnet field strengths measured in teslas or “T”, usually between 0.5T and 3.0T. The higher the “T” the greater the image quality and resolution. However, too much detail can be inappropriate or unnecessary parts of the anatomy. MRI scanners also come in varying sizes including open and wide-open.
To learn how we minimize radiation, please click here.
-
Diagnostic Radiology, General Ultrasound, Vascular Ultrasound, MRI, CT Scan, X RayDr. Daniel Beyda is a highly trained Board Certified Radiologist. He earned his medical degree and an MA in Medical Sciences...

What is a CT scan?
A CT (computed tomography) scan is an advanced type of X-ray exam. Multiple X-rays are taken rapidly from a number of different angles around the body and then arranged by a high-speed computer to produce a cross-sectional view. CT may be used to visualize internal organs, head, neck, spine, or extremities.
For some CT scans, the radiologist injects intravenous contrast medium or dye to highlight certain tissues for closer examination. Certain patients may also be required to drink oral contrast as well. A CT scan helps differentiate between healthy and diseased tissue, making it possible to accurately diagnose many diseases in their early stages.
When is a CT scan used?
CT scanning is generally used when your doctor needs more detailed diagnostic information than is possible from regular X-ray studies.
What happens during a CT scan procedure?
You will be positioned onto the table for the scan. You will feel the table move after each scan and may hear a whirring noise or high-pitched beep.
To get the most precise results, the technologist may ask you to hold your breath for a short time. Lie as still as possible to avoid blurring the images. You will be able to communicate with the technologist at all times during your scan. The actual time to acquire the images is often less than two minutes, but you should expect to be in the imaging room for approximately 10 to 15 minutes in its entirety.
You may leave immediately after your CT scan. If contrast was used, drink plenty of fluids, especially water, for the next 24 hours to help flush the contrast medium from your body. The radiologist will review your scans and send the results to your physician. Urgent findings will be called or faxed to your physician very shortly after completion of your study.
What are the benefits and risks of a CT scan?
CT scans are among the safest exams we do. Your body will be exposed to a very small amount of radiation. If you are pregnant, you should not have a CT scan without first discussing the risks with your doctor. There is a small risk you will have an allergic reaction to contrast dye. Common minor allergic reactions may include hives and itching. More serious contrast reactions are very rare. Be sure to tell your health care provider if you know you are allergic to any medications or chemicals such as iodine. Our staff and physicians are trained and prepared to handle immediately any allergic reaction you might have and prevent any future occurrences.
To learn how we minimize radiation, please click here.
-
Diagnostic Radiology, General Ultrasound, Vascular Ultrasound, MRI, CT Scan, X RayDr. Daniel Beyda is a highly trained Board Certified Radiologist. He earned his medical degree and an MA in Medical Sciences...

What is a digital X-ray?
X-ray is the oldest and most frequently used form of medical imaging. It is also the fastest and easiest and most economical way for a physician to view and assess broken bones.
It can also be used to diagnose and monitor the progression of diseases, including osteoporosis, heart disease, and cancer. Unlike other forms of radiation, X-rays can easily pass through body tissue, making it possible to provide images of internal structures without performing surgery.
During the procedure, electromagnetic radiation passes through the body onto “film” (now digitized and displayed on a computer screen). Dense structures such as bone absorb most of the radiation and appear white on the digital image. Structures that are less dense like air appear black. Everything in between appears a different shade of gray.
When is a digital X-ray used?
Digital X-rays are used to diagnose a wide range of illnesses and injuries, including musculoskeletal injuries, cancer, blocked arteries, abdominal pain, sinus disease, spinal problems, and other abnormalities.
What happens during a digital X-ray procedure?
You may be asked to stand or lie down on an examination table, depending on the part of the body to be examined. You will be able to communicate with the technician during the procedure.
What are the benefits and risks of a digital X-ray?
There is little reason to worry about the small amount of radiation you will be exposed to when you receive a digital X-ray. Digital X-rays enable immediate diagnosis of certain conditions and offer no discomfort, and often even no preparation, for the patient.
Why digital?
We use the most advanced technology to deliver premium healthcare. Digital imaging gives us many advantages in handling your exam, not the least of which is faster communication of results to your doctor. Digital imaging also allows your medical team to collaborate, if necessary, and to immediately compare previous exams with current ones, so that your health is properly monitored.
To learn how we minimize radiation, please click here.
-
Diagnostic Radiology, General Ultrasound, Vascular Ultrasound, MRI, CT Scan, X RayDr. Daniel Beyda is a highly trained Board Certified Radiologist. He earned his medical degree and an MA in Medical Sciences...